Mark Stengler N.M.D
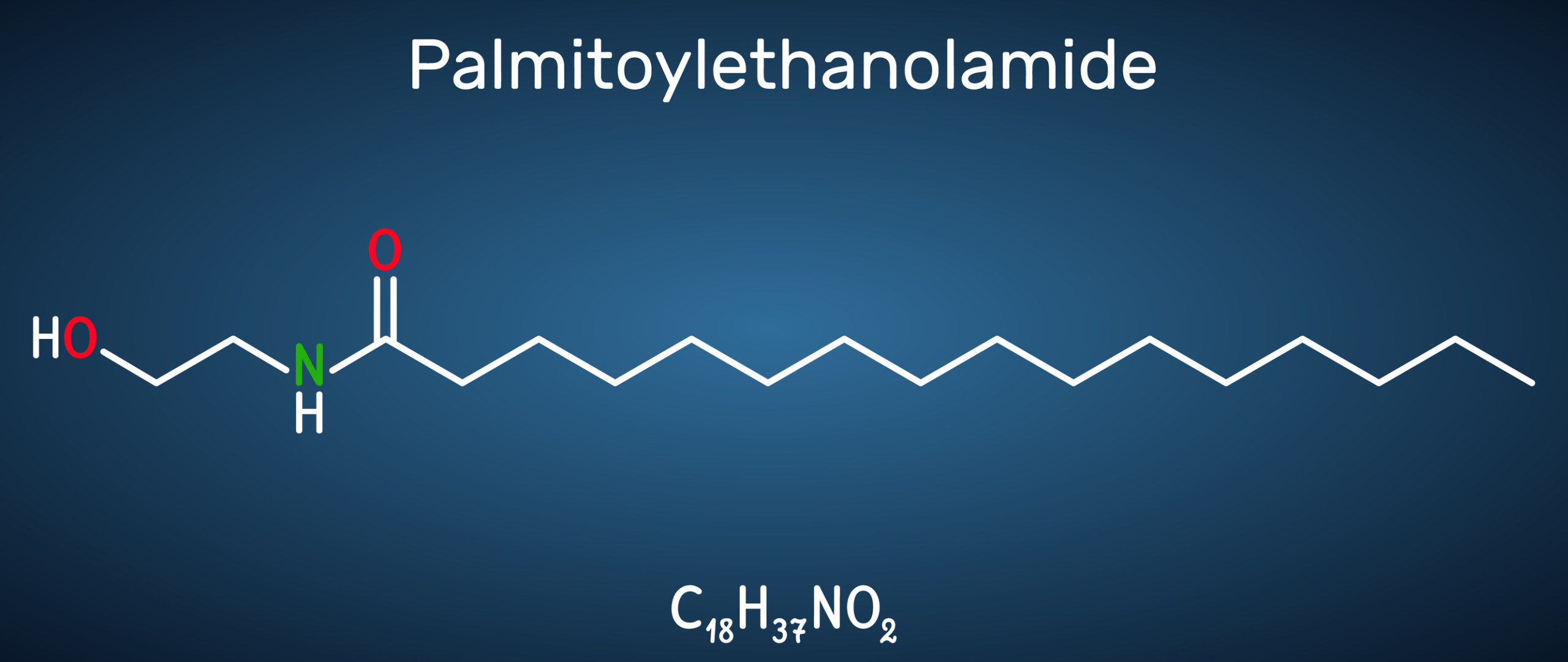
A breakthrough in pain and inflammation support has arrived on the natural health market. PEA, which stands for palmitoylethanolamide, is a naturally occurring fatty acid derivative made in the body and found in small amounts in foods. Several human studies have demonstrated that PEA has broad- spectrum pain-relieving properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and nerve protection. Now, consumers can access a natural substance to help manage pain and inflammation.
Multiple studies have demonstrated that PEA improves all sorts of pain. For example, a 2023 analysis of 11 studies found that PEA improved pain of various conditions, including muscle and joints, nerves, gynecological, and digestive. In terms of joint pain, a high quality study demonstrated that PEA significantly reduced adult joint pain compared to placebo. Moreover, 8 clinical trials demonstrated that PEA was effective for low back pain, sciatica, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Even migraine headache pain was shown in published research to be improved with PEA.
A technology that improves intestinal absorption has solved the problem of low PEA absorption. This form of PEA is known as Levagen TM , which is 75% more bioavailable than regular PEA. Emerald Labs PEA+ uses this form as the lead ingredient in its formula. Moreover, PEA has been shown to have a very high safety rating. Additional pain and inflammation-fighting ingredients include highly absorbable turmeric and highly purified MSM. This formula by Emerald Labs offers the public a more natural way to help manage and resolve chronic pain and inflammation.
Learn more about Emerald Labs PEA+
Use the code: Forever to get 20% Off
References
Briskey, D., Roche, G., & Rao, A. (2021). The effect of a dispersible palmitoylethanolamide (Levagen+)
compared to a placebo for reducing joint pain in an adult population – a randomised, double-blind
study. International Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences, 10(1), 9.
https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijnfs.20211001.12
Keppel Hesselink, J. M., & Kopsky, D. J. (2015). Palmitoylethanolamide, a nutraceutical, in nerve
compression syndromes: efficacy and safety in sciatic pain and carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of Pain
Research, 8, 729–734. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S93106
Lang-Illievich, K., Klivinyi, C., Lasser, C., Brenna, C. T., Szilagyi, I. S., & Bornemann-Cimenti, H. (2023).
Palmitoylethanolamide in the treatment of chronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
double-blind randomized controlled trials. Nutrients, 15(6), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061350
Pickering, E., Steels, E. L., Steadman, K. J., Rao, A., &Vitetta, L. (2022). A randomized controlled trial
assessing the safety and efficacy of palmitoylethanolamide for treating diabetic-related peripheral
neuropathic pain. Inflammopharmacology, 30(6), 2063–2077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-